Hot to get rid of Thrush and Yeast Infection?
Many people confuse thrush and yeast infections, but they are very different. While both may cause symptoms like white discharge, itching, and a burning sensation in the vagina, yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of a fungus called Candida albicans. Thrush, on the other hand, is caused by an overgrowth of bacteria called Candida tropicalis. Candida species are naturally occurring and can be found on moist, exposed surfaces like the inside of your mouth, the vaginal area, and the diaper area of babies.
The problem comes when the fungus grows too much, and you get infected. This usually happens when taking medications or doing something that changes your natural balance of microorganisms.
Is thrush and yeast infection the same thing?
No, but they can be caused by the same things. Thrush is an infection that affects your vagina, while a yeast infection affects your entire body.
What causes female thrush?
Thrush occurs when there’s an overgrowth of Candida albicans—a type of fungus that lives in your vaginal area. Yeast infections occur when Candida albicans overgrow in other parts of your body (like your mouth or throat). These infections may look similar to each other, but they have different causes. What’s more, thrush and yeast infection symptoms may differ in each person.
Thrush and Yeast Infection – symptoms
Thrush and yeast infections are itchy and may give an uncomfortable, burning sensation. There may be a whitish discharge. For example, some people have itching or burning when they have a yeast infection—but not with thrush. Other people may experience pain during intercourse if they have a yeast infection but not if they have thrush (which is why it’s essential to see your doctor if you suspect you may be infected).
You may have a yeast infection if you notice:
- white discharge that looks like cottage cheese or yogurt (it’s often creamy and curd-like)
- itching or burning in your vagina
- pain when you pee
- pain during sex
A breastfeeding mother with thrush will have nipples & areola that are itchy and red, and the skin flakes.
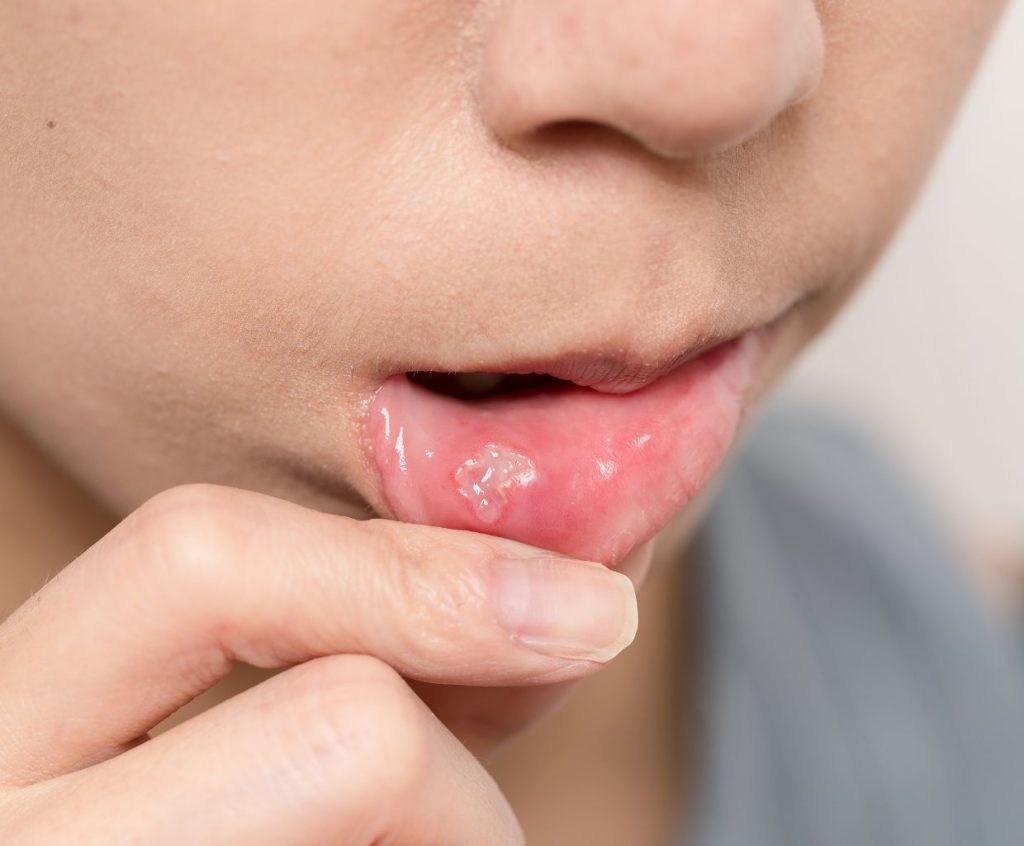
In a baby, thrush can be seen as white patches inside his mouth. He may be fussy, refuse to nurse, and have a diaper rash.
How to Cure Thrush and Yeast Infection
Generally speaking, the only way to get rid of thrush is to see your doctor and get some medicine. Because thrush is a yeast infection (not a bacterial infection), it is hard to get rid of and may take weeks of treatment. In addition to treating the condition, it may be wise to examine your lifestyle to see why and how you got the infection in the first place. Knowing this may help you avoid getting re-infected again.
Thrush is usually treated with topical creams that contain antifungal medications. A doctor can prescribe these creams or purchase them over the counter at your local pharmacy. However, a yeast infection left untreated for too long can become chronic and lead to other problems like bacterial vaginosis or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
The leading cause of thrush is antibiotic use; if you’ve taken any antibiotics recently, you should see your doctor as soon as possible to get tested for this condition before it worsens! While thrush can be treated with a topical cream, it’s best to get checked out by your doctor first. Not only will they prescribe the proper treatment for you, but they’ll also rule out any other infections that could be causing your symptoms.
What happens to thrush if it is left untreated?
If you don’t treat thrush, it could lead to bacterial vaginosis or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can cause infertility and chronic pain in the abdomen or pelvis. So make sure you get treated ASAP!